Jul 01, 17 · After converting the odds ratio to a risk ratio, the actual risk is 14 (mortality is 14 times more likely in patients with ICU delirium compared to those without ICU delirium) Because the incidence rate in the nondelirium group is high, the odds ratio exaggerates the true risk demonstrated in the studyIn a control group The odds ratio (OR) is the odds of an event in an experimental group relative to that in a control group An RR or OR of 100 indicates that the risk is comparable in the two groups A value greater than 100 indicates increased risk;Dec 08, 18 · Risk Ratio vs Odds Ratio Whereas RR can be interpreted in a straightforward way, OR can not A RR of 3 means the risk of an outcome is increased threefold A RR of 05 means the risk is cut in half But an OR of 3 doesn't mean the risk is threefold;

When To Use Risk Ratio Vs Odds Ratio
Are odds ratio and hazard ratio the same
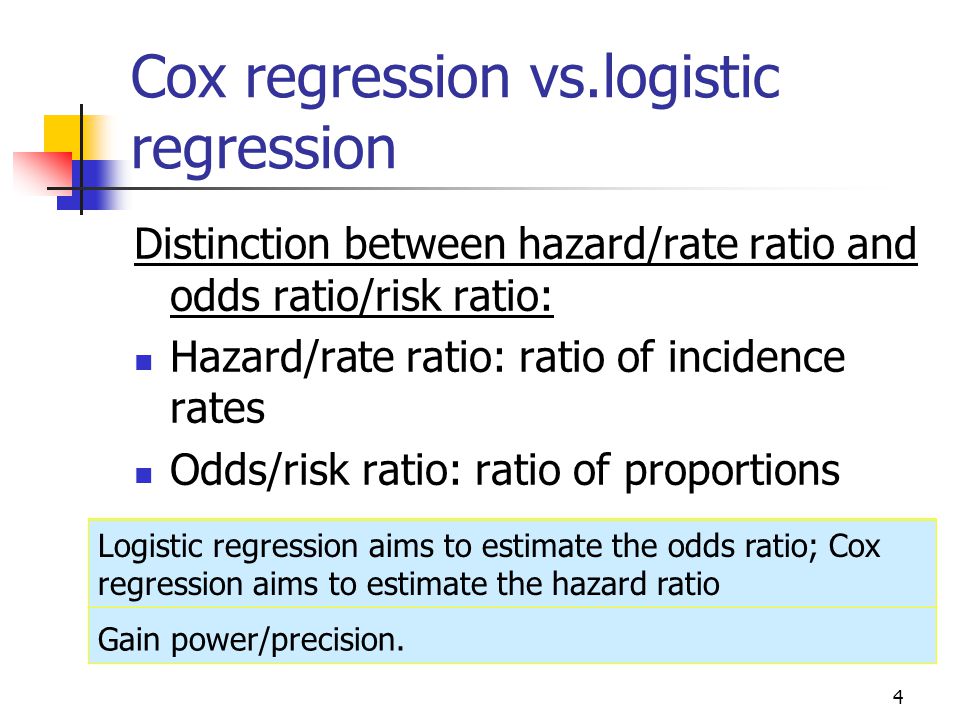
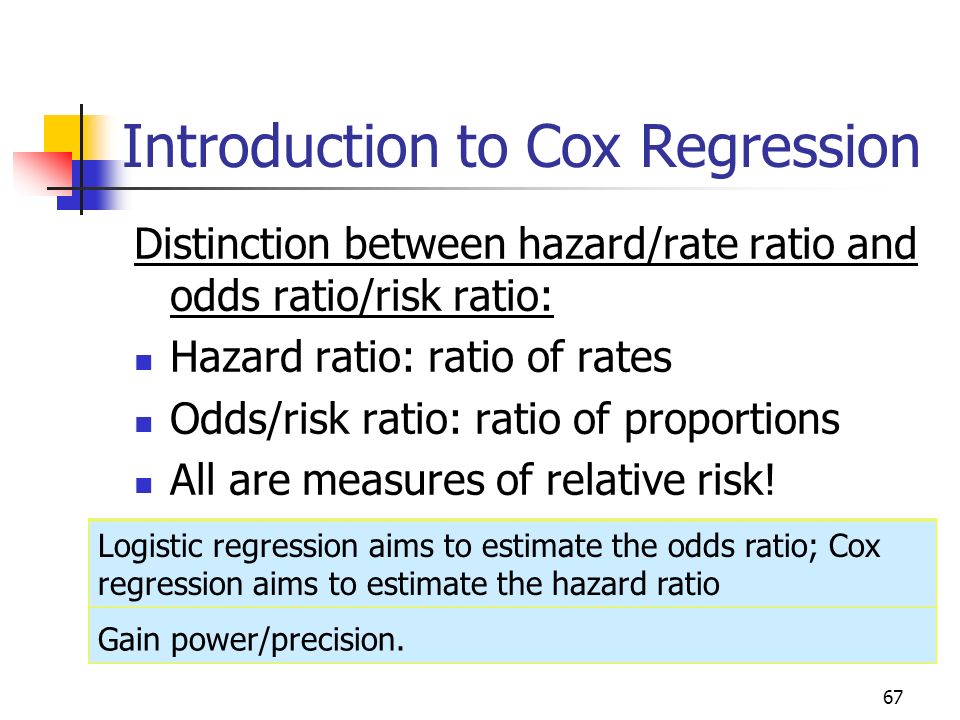
Are odds ratio and hazard ratio the same-Hazard ratios differ from relative risks (RRs) and odds ratios (ORs) in that RRs and ORs are cumulative over an entire study, using a defined endpoint, while HRs represent instantaneous risk over the study time period, or some subset thereof ;Cox regression vs logistic regression Distinction between hazard/rate ratio and odds ratio/risk ratio – Hazard/rate ratio ratio of incidence rates – Odds/risk ratio ratio of proportions By taking into account time, you are taking into account more information than just binary yes/no Gain power/precision



Jci Insight Plasma Copeptin And Chronic Kidney Disease Risk In 3 European Cohorts From The General Population
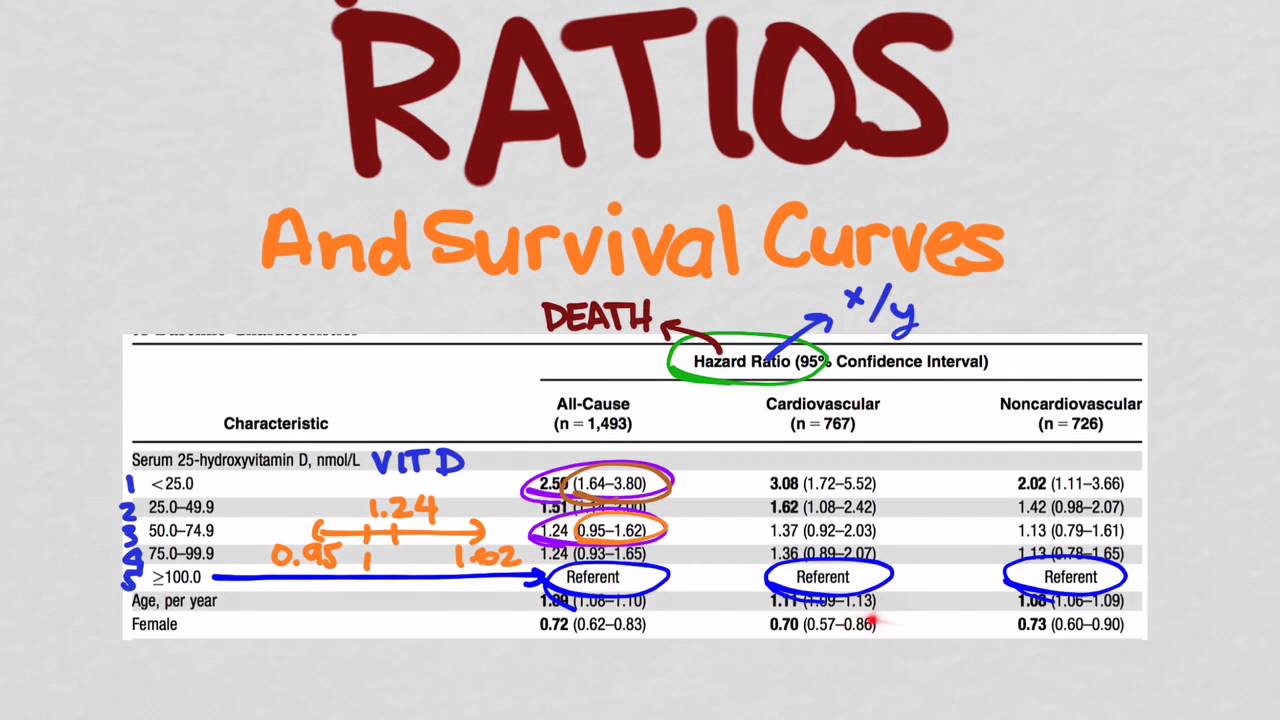
May 04, 09 · A crude odds ratio can be converted to a crude risk ratio risk ratio = odds ratio/(1 − p0) (p0 × odds ratio), in which p0 is the outcome prevalence (risk) among the unexposed Some have applied this formula to an adjusted odds ratio to obtain an adjusted risk ratio 49 This method can produce biased risk ratios and incorrect confidence intervals 26 , 32And the statistic given was "hazard ratio 0 (95% CI , p value=0013)Risk, absolute risk, odds ratio and hazard ratio These figures help to determine if the new treatment has an advantage over other treatments or placebo Ways of expressing treatment effects The absolute risk, number needed to treat, relative risk and odds ratio can be calculated by compiling a 2x2 table of study data
HR > 1 increase in the hazard;Odds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively understand as a measure of association Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a risk ratio (RR) In casecontrol studies, andFeb 17, 21 · Hazard ratios Hazard ratios are calculated using survival data and survival analysis You would use this if you have a oneoff event as your outcome (for example, death, cancer diagnosis, or discharge from hospital) and follow people up for a variable amount of time Hazard ratio = (hazard rate in intervention group) / (hazard rate in control group)
Rather the odds is threefold greater Interpretation of an OR must be in terms of odds, notPeto's method applied to dichotomous data (Section 9442) gives rise to an odds ratio;1 Log hazard ratio of dropout from the maintenance treatment program between patients in clinics B and A who take 50mg dose of methadone 2 Log hazard ratio of dropout from the maintenance treatment program between two individuals who are at clinic A and whose dosage differs by 1 mg 3 Difference in log hazard ratio of dropout from the



Approximate Reciprocal Relationship Between Two Cause Specific Hazard Ratios In Covid 19 Data With Mutually Exclusive Events Medrxiv


Plos One Pcsk9 Loss Of Function Variants And Risk Of Infection And Sepsis In The Reasons For Geographic And Racial Differences In Stroke Regards Cohort
Odds Ratio (OR) measures the association between an outcome and a treatment/exposure Or in other words, a comparison of an outcome given two different groups (exposure vs absence of exposure) OR is a comparison of two odds the odds of an outcome occurring given a treatment compared to the odds of the outcome occurring without the treatmentThe hazard ratio would be 2, indicating higher hazard of death from the treatment Hazard ratios differ from relative risks (RRs) and odds ratios (ORs) in that RRs and ORs are cumulative over an entire study, using a defined endpoint, while HRs represent instantaneous risk over the study time period, or some subset thereof Hazard ratios suffer somewhat less from selection bias withNov , 18 · To the Editor Dr Norton and colleagues 1 described significant limitations of odds ratios (ORs) but they did not report one important advantage of ORs compared with risk ratios (RRs) the magnitude of the association between an exposure and a dichotomous outcome is invariant to whether the outcome is defined as event occurrence (eg, death) or nonoccurrence


Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk Janez Stare Semantic Scholar


Forest Plots Of Hazard Ratios Hrs For Overall Survival A And Odds Download Scientific Diagram
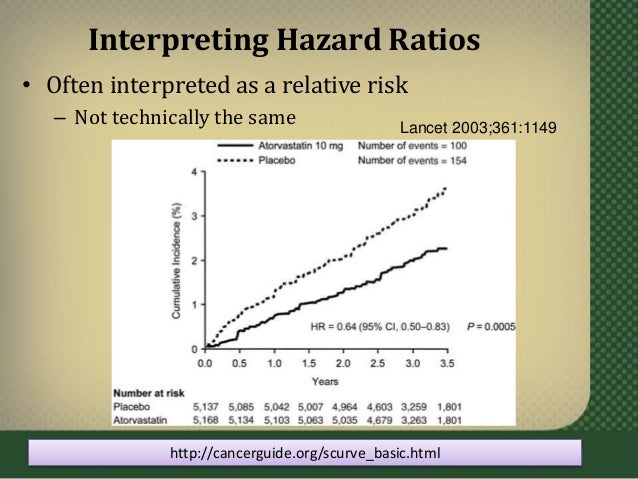
Apr 05, 19 · Let's say that in your experiment the calculated Hazard Ratio is equal to 065 This is how you can interpret and report it The mortality rate in a group of smokers drops by 35% compared to the group of highcalorie diet The mortality rate among smokers is 065 times of that among patients with a highcalorie dietHazard ratio, odds, and probability of healing There is an alternative interpretation of the hazard ratio that may be intuitively easier to understand The hazard ratio is equivalent to the odds that an individual in the group with the higher hazard reaches the endpoint first Thus, in a clinical trial examining time to disease resolution, itAug 13, 13 · I just have a question regarding hazard ratios Are these similar to odds ratio?



Hazard Ratio Wikipedia



Lincom Stata
This is called the odds ratio;Intervals and statistical vs clinical significance This second article will discuss absolute and relative risks, number needed to treat and harm, KaplanMeier survival curves and understanding diagnostic tests What are absolute risks, relative risks, odds ratios and hazard ratios?HR < 1 reduction in the hazard Moving again on the R code, we can see (by means of the summary function) the hazard ratios for the covariates included in the model



Crude And Adjusted Measures Of Odds Ratio Or And Hazard Ratio Hr Download Table



Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence
An odds ratio greater than 1 indicates that the condition or event is more likely to occur in the first group And an odds ratio less than 1 indicates that the condition or event is less likely to occur in the first group The odds ratio must be nonnegative if it is defined It is undefined if p 2 q 1 equals zero, ie, if p 2 equals zero or qAbout Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us CreatorsThe odds ratio ((a/c)/(b/d)) looks at the likelihood of an outcome in relation to a characteristic factor In epidemiological terms, the odds ratio is used as a point estimate of the relative risk in retrospective studies Odds ratio is the key statistic for most casecontrol studies



Fillable Online Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk Fax Email Print Pdffiller



Measures Of Association Ppt Download
A value lower than 100 indicates decreased risk The 95% confidence intervals and statisticalA logrank approach gives rise to a hazard ratio, and a variation of the Peto method for analysing timetoevent data gives rise to something in between The appropriate effect measure should beApr 05, 16 · Hazard Ratio (ie the ratio of hazards) = Hazard in the intervention group ÷ Hazard in the control group Hazard represents the instantaneous event rate, which means the probability that an individual would experience an event (eg death/relapse) at a particular given point in time after the intervention, assuming that this individual has survived to that particular point of time
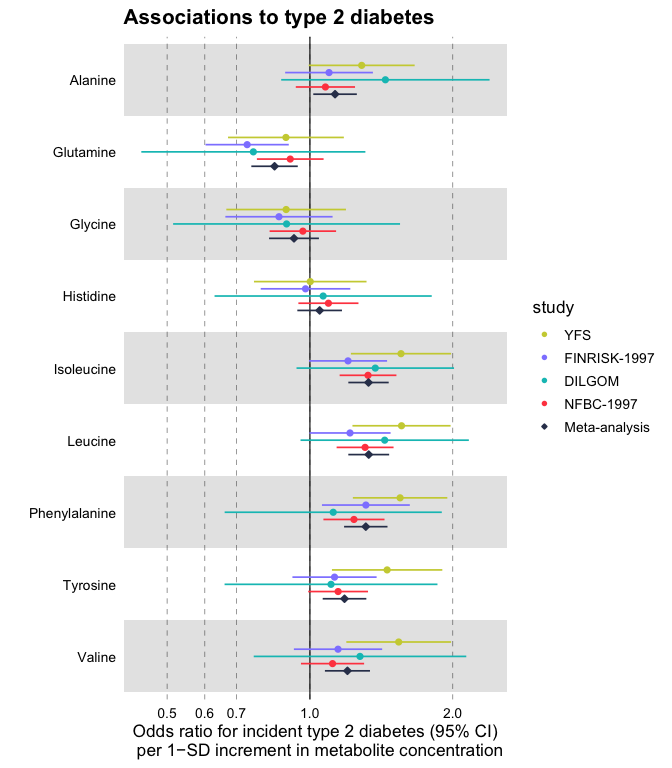


Forestplots Of Measures Of Effects And Their Confidence Intervals Ggforestplot



What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora
Jun 01, 11 · Hazard ratio (E vs C) for the time period Please note that results shown are rounded to 2 decimal places, but the calculations used the raw numbers from the previous column (c) and therefore give different results than if the rounded numbers were used (eg, 006/008 = 075)Variable on the hazard or risk of an event Hazard ratio can be considered as an estimate of relative risk, which is the risk of an event (or of developing a disease) relative to exposureRelative risk is a ratio of the probability of the event occurring in the exposed group versus the control (nonexposed) groupMay 18, 12 · The risk ratio is less than 10, indicating a decreased risk or protective effect for the exposed (vaccinated) children The risk ratio of 028 indicates that vaccinated children were only approximately onefourth as likely (28%, actually) to develop varicella as


Hazard Ratios


Medical Statistics And Data Science Statistics
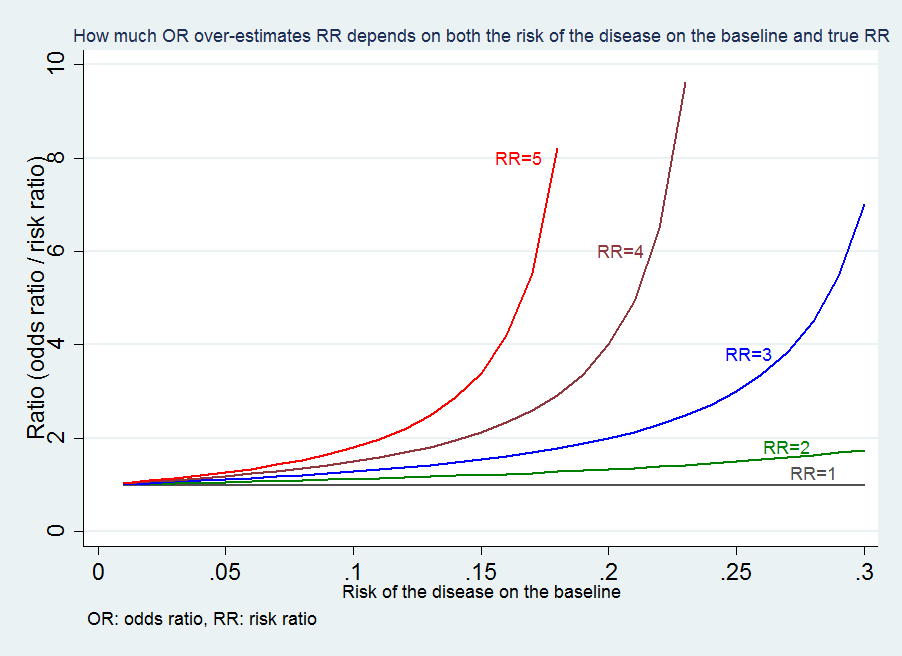
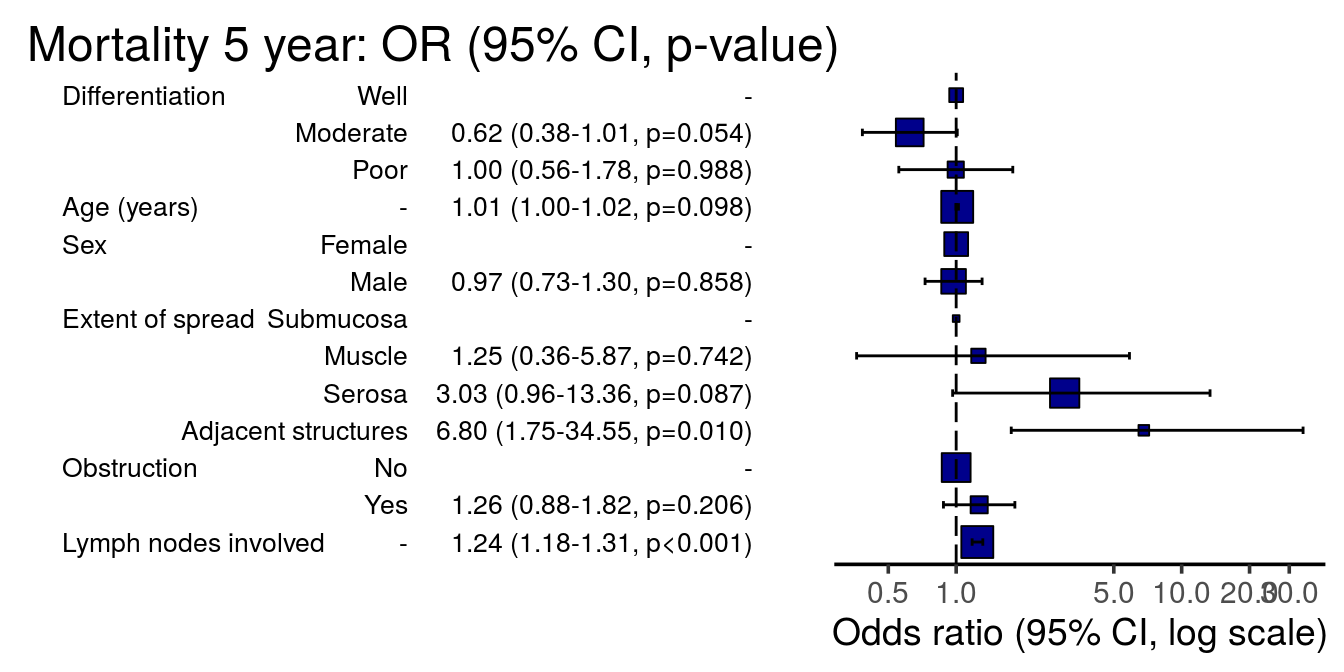
13 an odds ratio of 2 means that the event is 2 time more probable given a oneunit increase in the predictor It means the odds would double, which is not the same as the probability doubling In Cox regression, a hazard ratio of 2 means the event will occur twice as often at each time point given a oneunit increase in the predictor Aside a bit of handwaving, yes the rate of occurrence3) The Odds Ratio 4) After calculating the odds ratio, we observe a 3fold difference in the prevalence rate (75% vs 25%) change to a 9fold difference in the odds ratio Clearly, the two methods produce opposing results Effect of Changing Incidence on OR Problem Let us consider the relationship between smoking and lung cancerFor instance, a disease free survival was longer for an anastrozole group compared to a tamoxifen group;



Hazard And Odds Ratios Image Eurekalert Science News



Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios
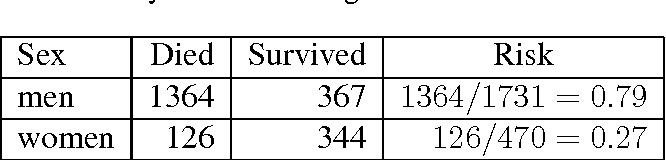
May 14, 19 · L'Odds Ratio (OR) est le rapport des cotes d'exposition Cette notion de cote est semblable à celle utilisée pour les paris sportifs Dans notre exemple la cote chez les personnes exposées est de 30 contre 70 Chez les non exposés, cette cote est de 10 pour 90Sep 02, · The risk or odds ratio is the risk or odds in the exposed group divided by the risk or odds in the control group A risk or odds ratio = 1 indicates no difference between the groups A risk or odds ratio > 1 indicates a heightened probability of the outcome in the treatment group The two metrics track each other, but are not equalSometimes, we see the log odds ratio instead of the odds ratio The log OR comparing women to men is log(144) = 036 The log OR comparing men to women is log(069) = 036 log OR > 0 increased risk log OR = 0 no difference in risk log OR < 0 decreased risk Odds Ratio 0 5 10 15 More on the Odds Ratio Log Odds Ratio4 2 0 2 4



Approximate Reciprocal Relationship Between Two Cause Specific Hazard Ratios In Covid 19 Data With Mutually Exclusive Events Medrxiv
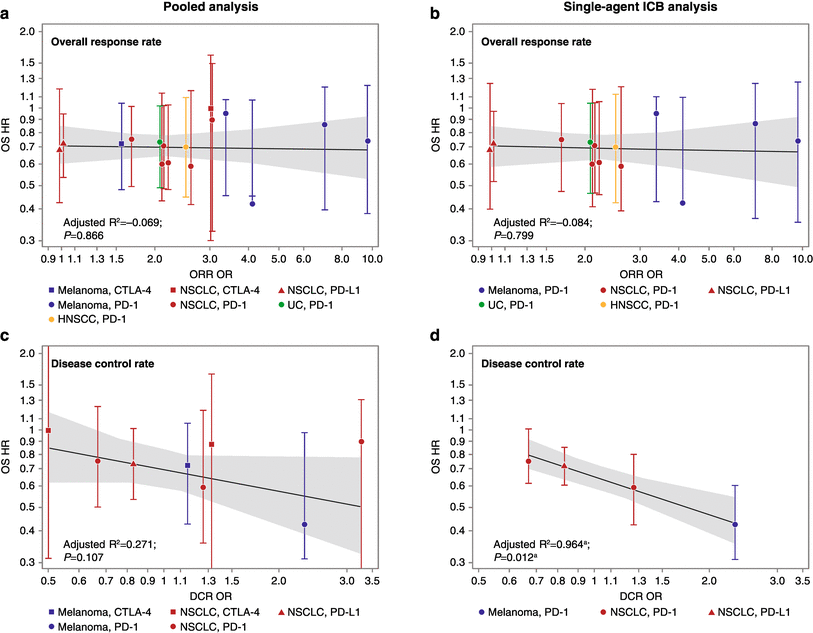


Figure 6 Evaluation Of Classical Clinical Endpoints As Surrogates For Overall Survival In Patients Treated With Immune Checkpoint Blockers A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis Springerlink
The method of presenting the results of clinical studies canIt is called that because it is the ratio of two odds Some people call the odds the odds ratio because the odds itself is a ratio That is fine English, but this can quickly lead to confusion If you did that, you would have to call this calculation the odds ratio ratio or the ratio of the odds ratiosJun 07, 07 · Odds ratios (ORs) or relative risks (RRs) that measure only the number of events and take no account of when they occur are appropriate for measuring dichotomous outcomes, but less appropriate for analysing timetoevent outcomes Using such dichotomous measures in a metaanalysis of timetoevent outcomes can pose additional problems



Statistics For Gp And The Akt Sept 11



Chapter 6 Choosing Effect Measures And Computing Estimates Of Effect Cochrane Training
Odds ratio, and when by equating the two statistics we are sometimes forcing OR to be something it is not Another statistic, which is often also perceived as a relative risk, is the hazard ratio (HR) We encounter it, for example, when we fit the Cox model to survival data Under proportional hazards it is probably "natural" to thinkHazard ratio The hazard ratio in survival analysis is the effect of an exploratory?Jul 11, 16 · The basic difference is that the odds ratio is a ratio of two odds (yep, it's that obvious) whereas the relative risk is a ratio of two probabilities (The relative risk is also called the risk ratio) Let's look at an example Relative Risk/Risk Ratio Suppose you have a school that wants to test out a new tutoring program



Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk 63 Table 5 Examples Of Rr And Or For Different Probabilities ˇ 1 ˇ 2 Rr Or 4 1 4 6 2 3 67 58 04 Pdf Document



Who Saw This In The San Francisco Chronicle In The Past Week Ppt Download
The relative risk and the odds ratio are measures of association between exposure status and disease outcome in a population Relative risk In epidemiology, relative risk (RR) can give us insights in how much more likely an exposed group is to develop a certain disease in comparison to a nonexposed group Once we know the exposure and disease status of a research population, we canFeb 01, 08 · In every other way the hazard ratio is similar to odds ratio and relative risk wherein treatment efficacy is denoted by a hazard ratio of less than 10 in prevention trials and a hazard ratio of more than 10 in treatment trials Table 3 Hazard ratio and timetoevent analysis 1Aug 26, · Risk ratios, odds ratios, and hazard ratios are three ubiquitous statistical measures in clinical research, yet are often misused or misunderstood in their interpretation of a study's results 1 A 01 paper looking at the use of odds ratios in obstetrics and gynecology research reported 26% of studies (N = 151) misinterpreted odds ratios as risk ratios 2, while a



Figure 2 From Events Per Person Time Incidence Rate A Misleading Statistic Semantic Scholar



What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean
Interpretation of the hazard ratio (like Odds Ratio in Logistic Models) HR = 1 no effect;The risk ratio (or relative risk) is the ratio of the risk of an event in the two groups, whereas the odds ratio is the ratio of the odds of an event (see Box 92a) For both measures a value of 1 indicates that the estimated effects are the same for both interventionsHazard ratio (E vs C) for the time period


Minerva



What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean
For studies that look at treatment effects or other effect sizes the program will compute the odds ratio, risk ratio, risk difference, standardized mean difference (d), biascorrected standardized mean difference (Hedges's g), raw mean difference, correlation, hazard ratio, rate ratio, and moreThe hazard ratio is simply the value of the hazard calculated from the treatment curve, divided by the hazard calculated from the control curve Based on the complexity, statistical software is required to make this calculation to estimate the hazard ratio Figure 1 The timetoevent curve or KaplinMeier curveAbout Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators
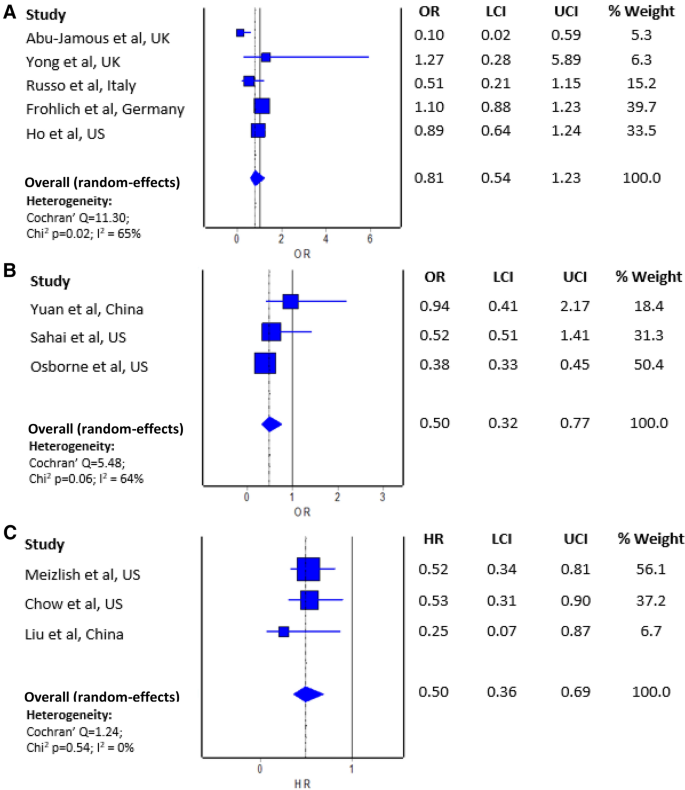


Use Of Antiplatelet Drugs And The Risk Of Mortality In Patients With Covid 19 A Meta Analysis Springerlink



Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk Janez Stare Semantic Scholar
Sep 18, · Log odds and log hazard ratios have an unlimited ranges and can possibly apply to everyone This makes them good bases for studying heterogeneity of treatment effect When risk factors exist and a clinical trial enrolls patients having a variety of values of these risk factors, there will be outcome heterogeneity



Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios


Statistics 262 Intermediate Biostatistics Ppt Video Online Download



Hazard Ratio Relative Risk Or Odds Ratio Of Selected Outcomes For The Download Table



Interpreting Hazard Ratios Youtube



Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio Et Risque Relatif Quelles Differences



Highly Customized Analytical Graphs



Research Techniques Made Simple Interpreting Measures Of Association In Clinical Research Sciencedirect


Plos One Influence Of Clinicopathological Characteristics And Comprehensive Treatment Models On The Prognosis Of Small Cell Carcinoma Of The Cervix A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis
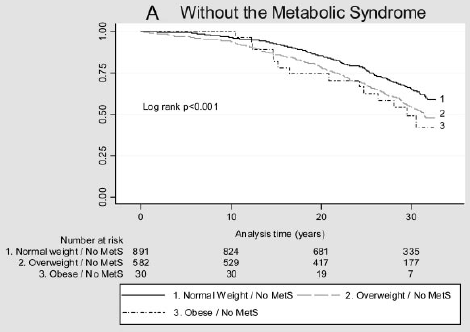


Lesson 13 Proportional Hazards Regression Stat 507



Outcomes Shown For A Odds Ratio Analysis And B Hazard Ratio Download Scientific Diagram



Jci Insight Plasma Copeptin And Chronic Kidney Disease Risk In 3 European Cohorts From The General Population



Related Image Cross Sectional Study Hazard Ratio Odds



On Biostatistics And Clinical Trials Understanding The Endpoints In Oncology Overall Survival Progression Free Survival Hazard Ratio Censored Value



Hazard Ratio An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



The Utility Of Mortality Hazard Rates In Population Analyses Biorxiv



Various Estimates For The Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Of Herpes Download Table


Tests For Time To Event Outcomes Survival Analysis Ppt Download



The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor


Hazard Ratios And Survival Curves Youtube



Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube



Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk Janez Stare Semantic Scholar



Graph Tip How Can I Plot An Odds Ratio Plot Also Known As A Forest Plot Or A Meta Analysis Plot Faq 809 Graphpad


Drmeta



1 Relative Risks Odds Ratios Or Hazard Ratios Of Risk Factors For Download Table



A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence



Introduction To Cox Regression Kristin Sainani Ph D



When To Use Risk Ratio Vs Odds Ratio


13 5 Odds Ratio Plot R For Health Data Science



Odds Ratio Wikipedia
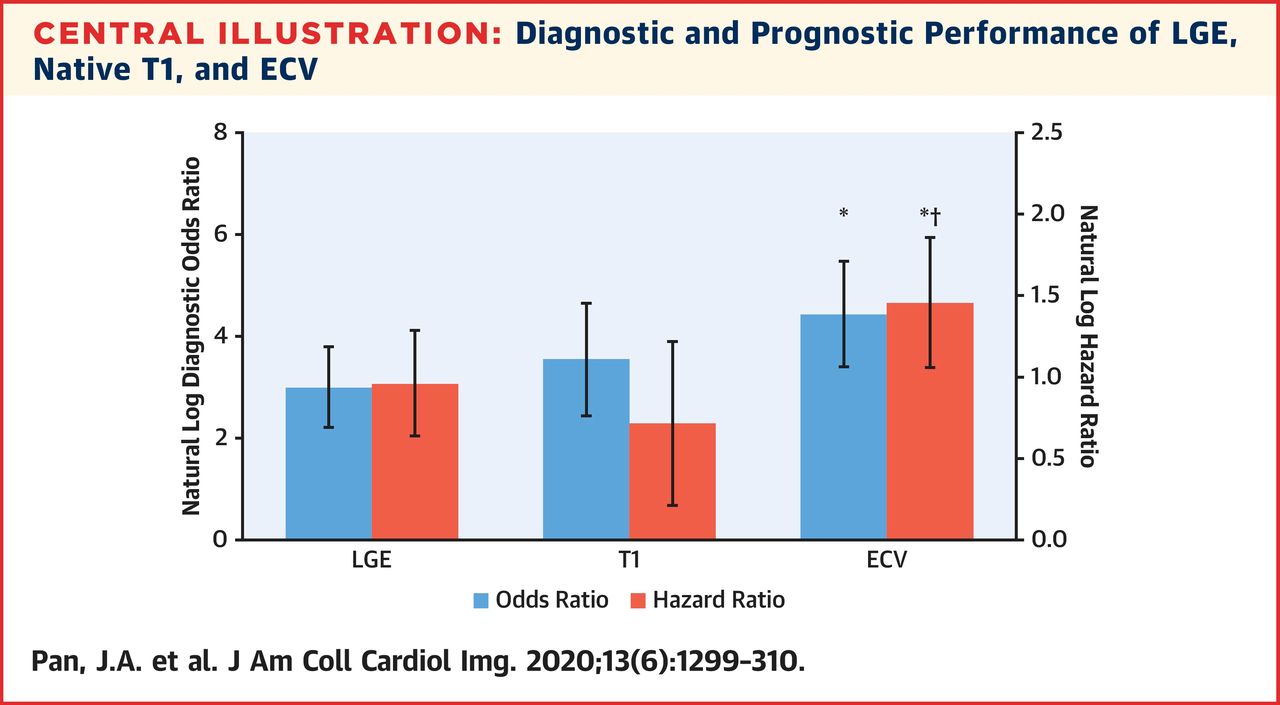


Jacc Journals Jaccimg Explores Cmr In Cardiac Amyloidosis T1 Mapping Has Similar Sensitivity Specificity While Avoiding Contrast Ecv Has Highest Diagnostic Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio For Adverse Events


Plos One Bleeding Risk With Long Term Low Dose Aspirin A Systematic Review Of Observational Studies


A Survival Analysis In The Assessment Of The Influence Of The Sars Cov 2 Pandemic On The Probability And Intensity Of Decline In The Value Of Stock Indices Springerlink



How To Be Awesome At Biostatistics And Literature Evaluation Part Ii Tl Dr Pharmacy



Ppt Point Estimation Odds Ratios Hazard Ratios Risk Differences Precision Powerpoint Presentation Id



Odds Ratio And Hazard Ratio For Complications Download Table


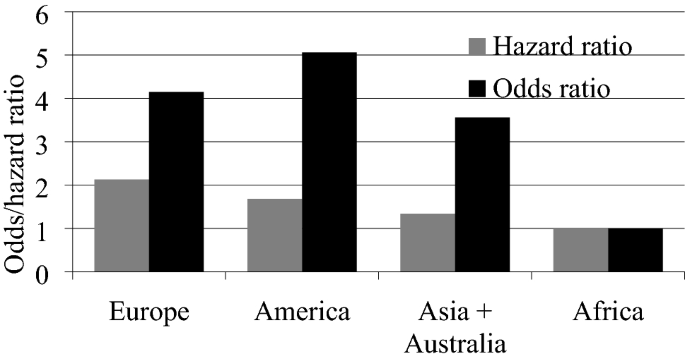
When To Use Hazard Ratio Vs Odds Ratio



Relaciones Entre Riesgo Relativo Hazard Ratio Y Odds Ratio Download Scientific Diagram



Crude And Adjusted Measures Of Odds Ratio Or And Hazard Ratio Hr Download Table



How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Youtube


How To Read A Forest Plot Cochrane Uk


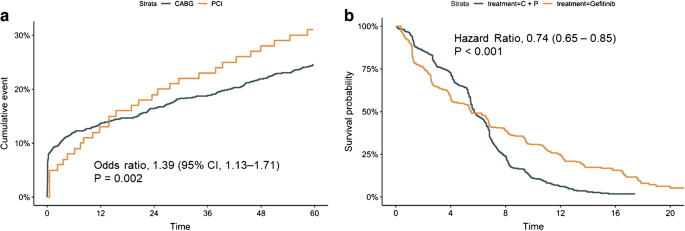
Prof Darrel Francis Mk Cardiofellows Great Again The Hazard Ratio Is In A Way The Best Thing We Could Calculate Because It Looks Along Every Instant In Time And


Calculating Population Attributable Fraction For Cardiovascular Risk Factors Using Different Methods In A Population Based Cohort Study Azimi Journal Of Research In Health Sciences



Clinical Trials In Hours Point Estimation Odds



What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean



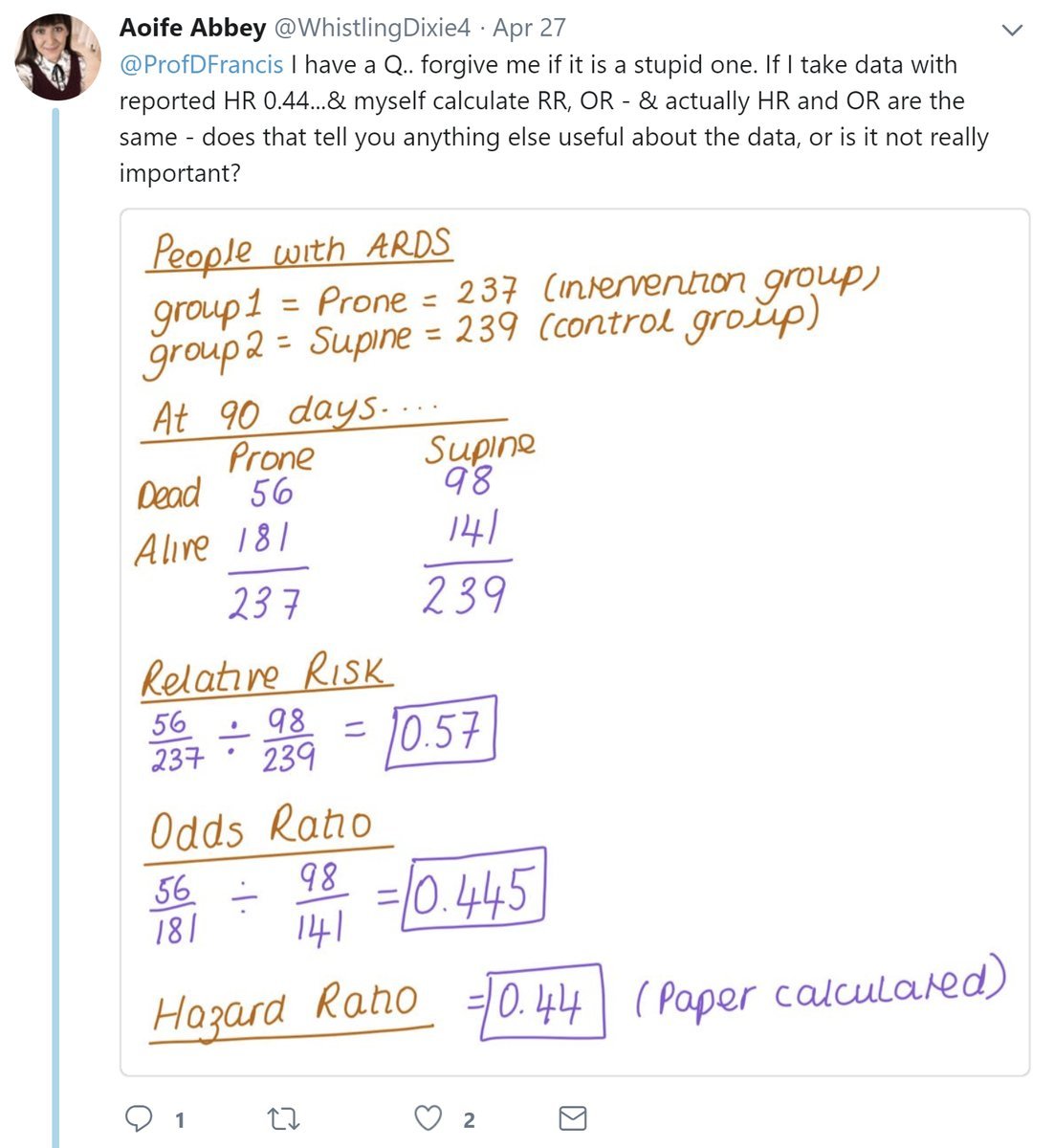
Thread By Profdfrancis Risk Ratio Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio 2nd And Final Part Of The Tweetorial From Orbita Hq Fun Easy And Informativ Meded Foamed Cardiology Cardiotwitter



Math3010 Week 6



Determinants Of Ex Ante Banking System Distress A Macro Micro Empirical Exploration Of Some Recent Episodes In Imf Working Papers Volume 1999 Issue 033 1999


Coefplot Plotting Regression Coefficients And Other Estimates In Stata



Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence
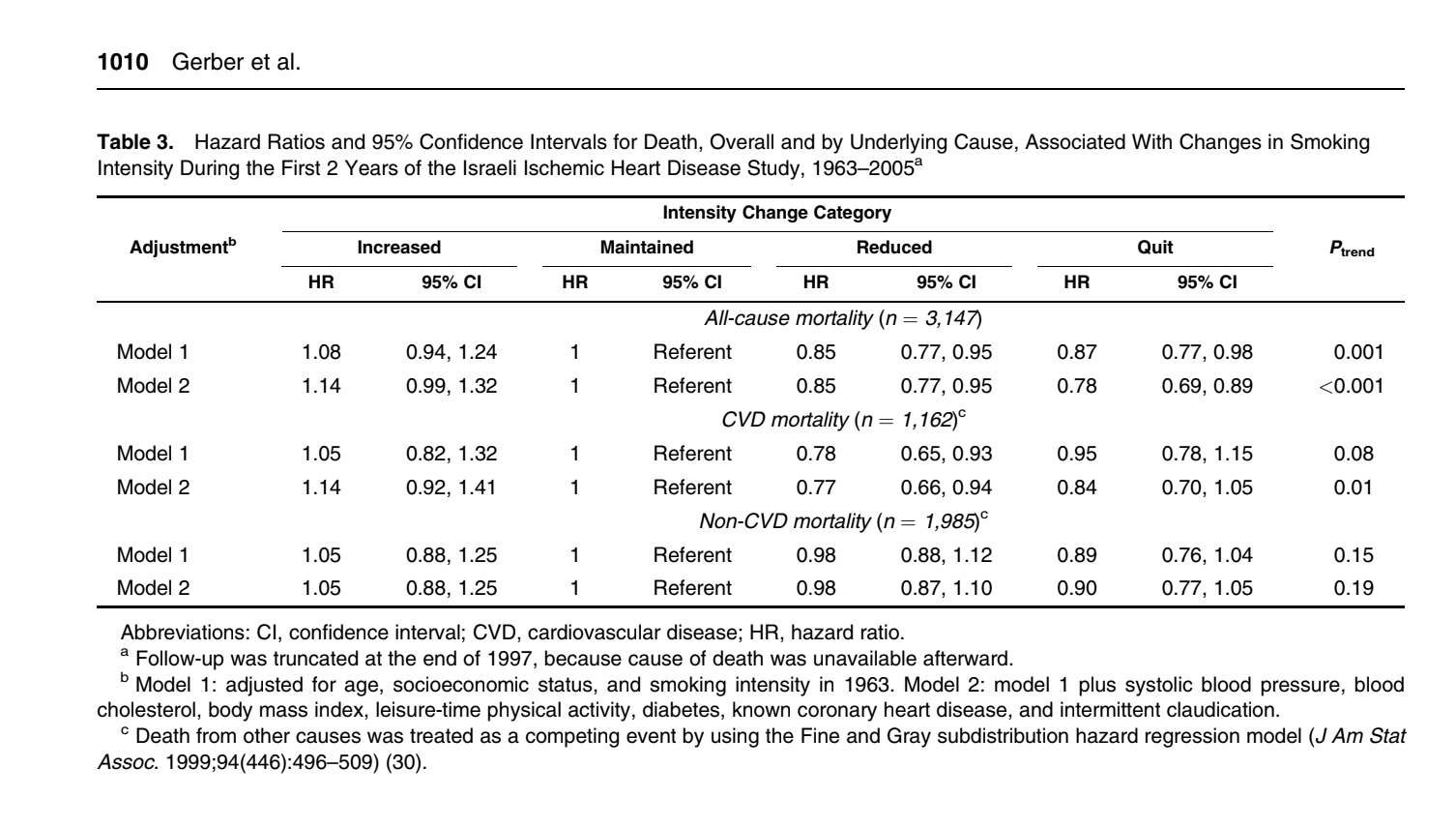


Solved Table 3 Provides Hazards Ratios 1 For The Reduce Chegg Com



Interpreting Odds Ratio Senguptas Research Academy



Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube
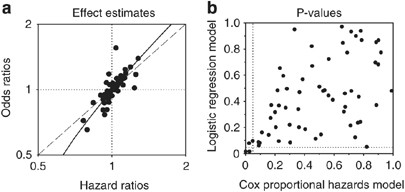


Cox Proportional Hazards Models Have More Statistical Power Than Logistic Regression Models In Cross Sectional Genetic Association Studies European Journal Of Human Genetics
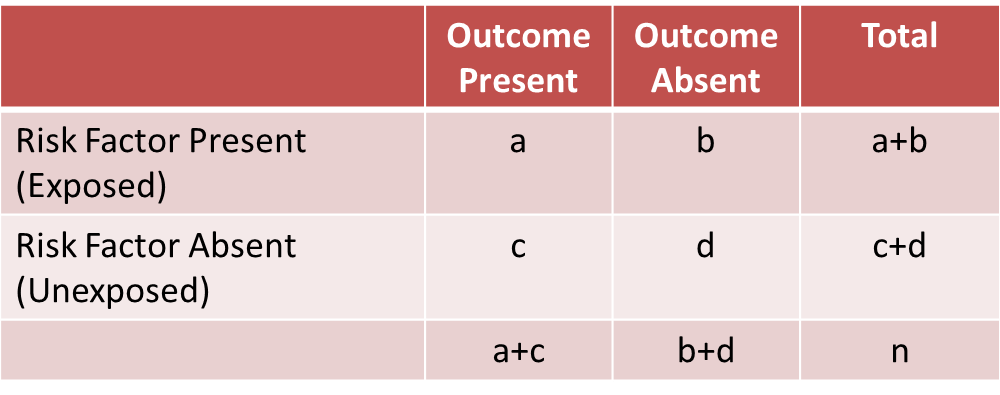


A Stratified Analysis



Effect Sizes Basicmedical Key



Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk Stat D Si Relative Risk Pdf4pro



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1
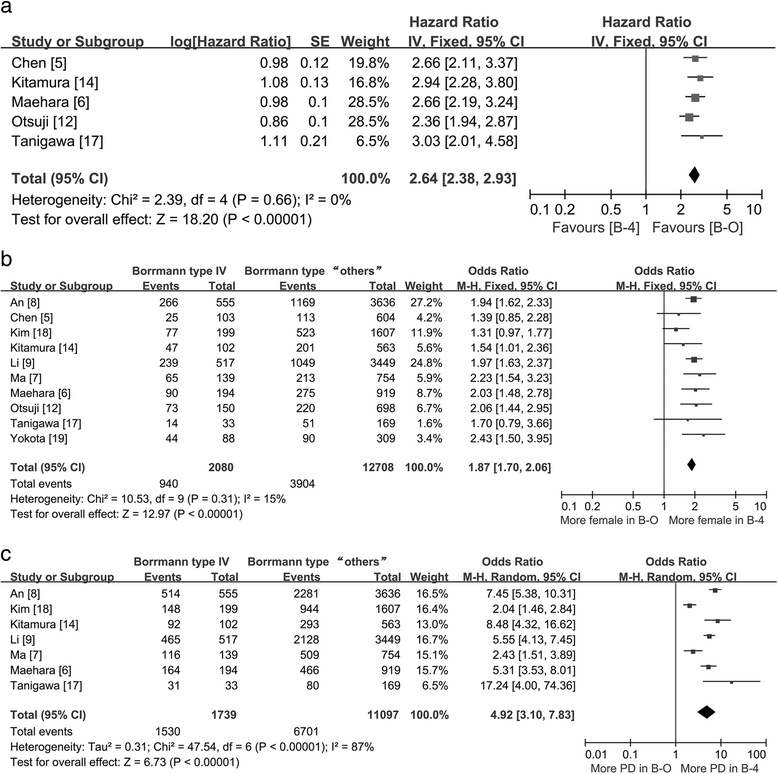


Clinicopathologic Characteristics And Prognosis Of Borrmann Type Iv Gastric Cancer A Meta Analysis World Journal Of Surgical Oncology Full Text



Interpreting Hazard Ratios Youtube



When To Use Odds Ratio Vs Hazard Ratio



Ctspedia Ctspedia Clinaegraph001



Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Sciencedirect



Odd Ratio Relative Risk Odds Ratio
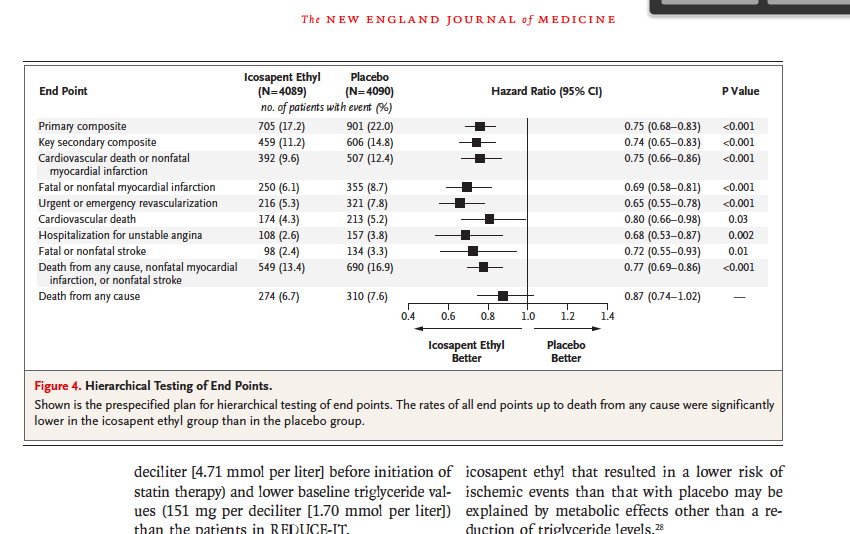


Solved State The Mean Median Hr Hazard Ratio Rr Chegg Com



Relative Risks And Odds Ratios What S The Difference Mdedge Family Medicine


